Eyelid Rejuvenation
About Eyelid Surgery (Blepharoplasty)
Blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery) is a plastic surgery procedure for correcting sagging or drooping eyelids. The skin is much thinner on the eyelid than that in other parts of the face, and therefore is often one of the first facial areas to exhibit signs of aging. Eyelids that sag or droop can affect peripheral vision, making daily activities such as driving more difficult. Blepharoplasty may become necessary when various factors, which include aging, sun damage, smoking and obesity, cause the muscles and tissue that support the eyelids to weaken.

Reasons For Eyelid Surgery
Blepharoplasty tightens the eyelid muscles and tissue, and removes excess fat and skin. Blepharoplasty eliminates the drooping of skin into the visual field, greatly improving peripheral vision. It is also performed for strictly cosmetic reasons. It is important for a patient to have realistic expectations before undergoing cosmetic blepharoplasty. Although the procedure can enhance appearance and improve self-confidence, it
does not radically alter the face.

Functional Blepharoplasty
If the eyelids begin sagging into the field of vision, a functional blepharoplasty may be required. The procedure may be covered by medical insurance if it is deemed medically necessary. A determination of how much vision is affected is done by checking the peripheral visual field with an instrument called the Humphrey Visual Field (HVF) Analyzer.
Cosmetic Blepharoplasty
Blepharoplasty can be performed on either the upper or lower eyelid, or on both, for cosmetic purposes. For a lower eyelid that needs fat rather than skin removed, a transconjunctival blepharoplasty is performed. During transconjunctival blepharoplasty, an incision is made inside the lower eyelid, so there are no visible scars, and the fat is removed. This procedure has no effect on vision, but results in a person looking younger and more refreshed.
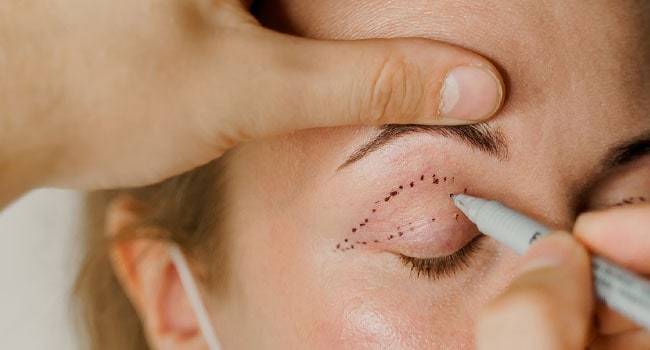
How is Blepharoplasty Performed?
Blepharoplasty is typically performed as an outpatient procedure requiring local anesthesia and sedation. General anesthesia may be used for anxious patients. Patients can choose to have this procedure on their upper or lower eyelids, or both. The procedure can take anywhere from 45 minutes to 2 hours, depending on whether both the upper and lower eyelids are operated on.
If the upper eyelid is being operated on, an incision is typically made along its natural crease. Once the incision is made, fat deposits are repositioned or removed, muscles and tissue are tightened, and excess skin is removed. For the lower eyelid, an incision is usually made just below the lash line so that excess skin can be removed.
After the procedure, the incisions are closed with sutures, tissue glue or surgical tape, and usually loosely covered with gauze so the area can heal.

Eyelid Surgery Aftercare & Recovery
After blepharoplasty, patients may be advised to apply lubricating drops/ointment and cold compresses to aid in healing and minimize side effects. Most patients return to work within a few days to a week, but should avoid exercise and strenuous activities for at least 2 weeks. Stitches are usually removed after 3 or 4 days. Most swelling and other side effects typically subside within 2 weeks. Contact lenses and eye makeup may not be worn for 2 weeks after surgery. Patients are typically advised to wear dark sunglasses outside or in bright light for 2 weeks to protect their eyes from sun and wind.
Blepharoplasty Risks
Most often there is swelling and bruising around the surgical site, which will subside on its own. The eyelids will improve in appearance for up to a year. Uncommon side effects include infection, reaction to anesthesia, and double or blurred vision. Eyes may be irritated and dry due to a temporary change in tear distribution. Side effects such as uneven healing and permanent scarring are rare but, if they occur, may require surgical correction. The scars from blepharoplasty are well-concealed, and usually fade with time until they are virtually undetectable. Although the eyelids are still subject to aging, blepharoplasty produces long-lasting results.
Eye Ptosis
Ptosis is the drooping of the upper eyelid caused by weakening of the muscles. While ptosis is usually the result of aging, some people develop ptosis after eye surgery or an injury, and the condition can be congenital. While ptosis may be present due to serious causes, treatment may not always be necessary. Patients should be evaluated by a medical professional.
Ptosis Causes
- Damage to the nerves
- Diabetes
- Migraine headache
- Stroke
- Growth in the eyelid, such as a stye
- Myasthenia gravis
- Horner syndrome
- Bell’s palsy
- Benign or malignant tumor
In rare instances, ptosis can occur due to a brain tumor or other malignancy that affects the reactions of muscles or nerves.


Ptosis Symptoms
Ptosis presents as the drooping of one or both eyelids and perhaps one or more of the following symptoms:
- Increased tear production
- Difficulty blinking or closing the eye
- Reduced vision (with severe drooping)
Since ptosis caused by aging is usually gradual, a sudden onset of symptoms is a greater cause for concern.
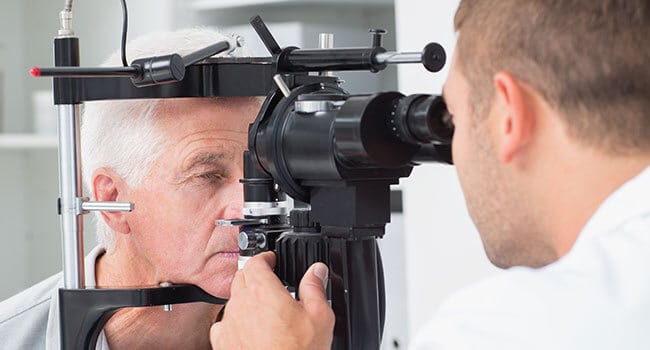
Ptosis Diagnosis
Ptosis is typically diagnosed by an ophthalmologist, who can also frequently determine the cause of the problem. In order to perform a comprehensive eye examination, the doctor may test visual acuity, perform visual field testing, a slit-lamp examination, and, possibly, a tension test for myasthenia gravis. If there is a suspicion of an underlying systemic disease, the patient will be referred to an internist or other physician for further investigation.
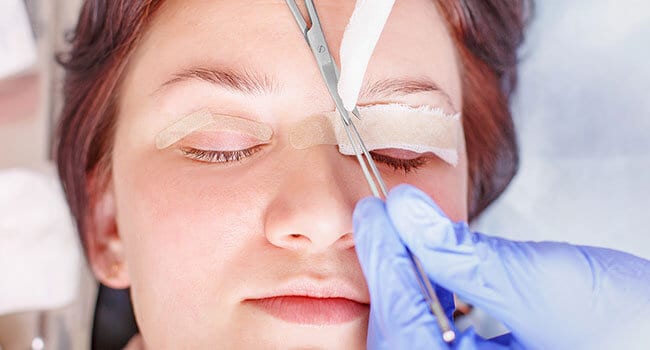
Ptosis Treatment
Patients may seek treatment for droopy eyelids for cosmetic or medical purposes. Severe drooping may obstruct vision as the eyelid gradually droops lower and lower, eventually covering the eye. If ptosis interferes with a patient’s vision, a blepharoplasty will be performed to eliminate the drooping. Many young patients with mild to moderate ptosis should be examined regularly to check for other vision problems including amblyopia, refractive errors, and muscular diseases.
To learn more about our eyelid rejuvenation procedures,
please contact us today at 585-328-0153